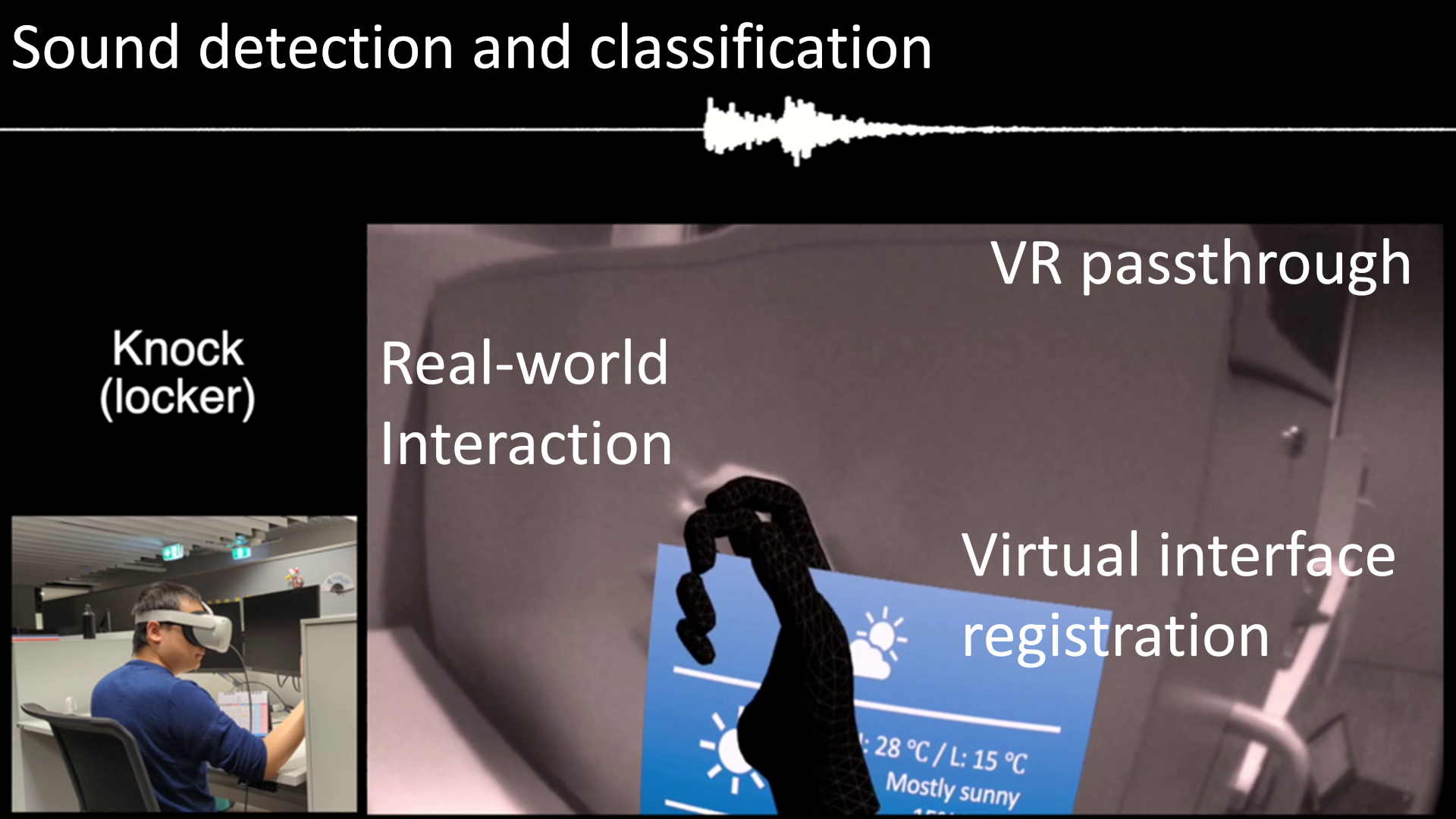
Knock the Reality: Virtual Interface Registration in Mixed Reality
Keywords: MR, Interaction, Prototyping, Deep learning
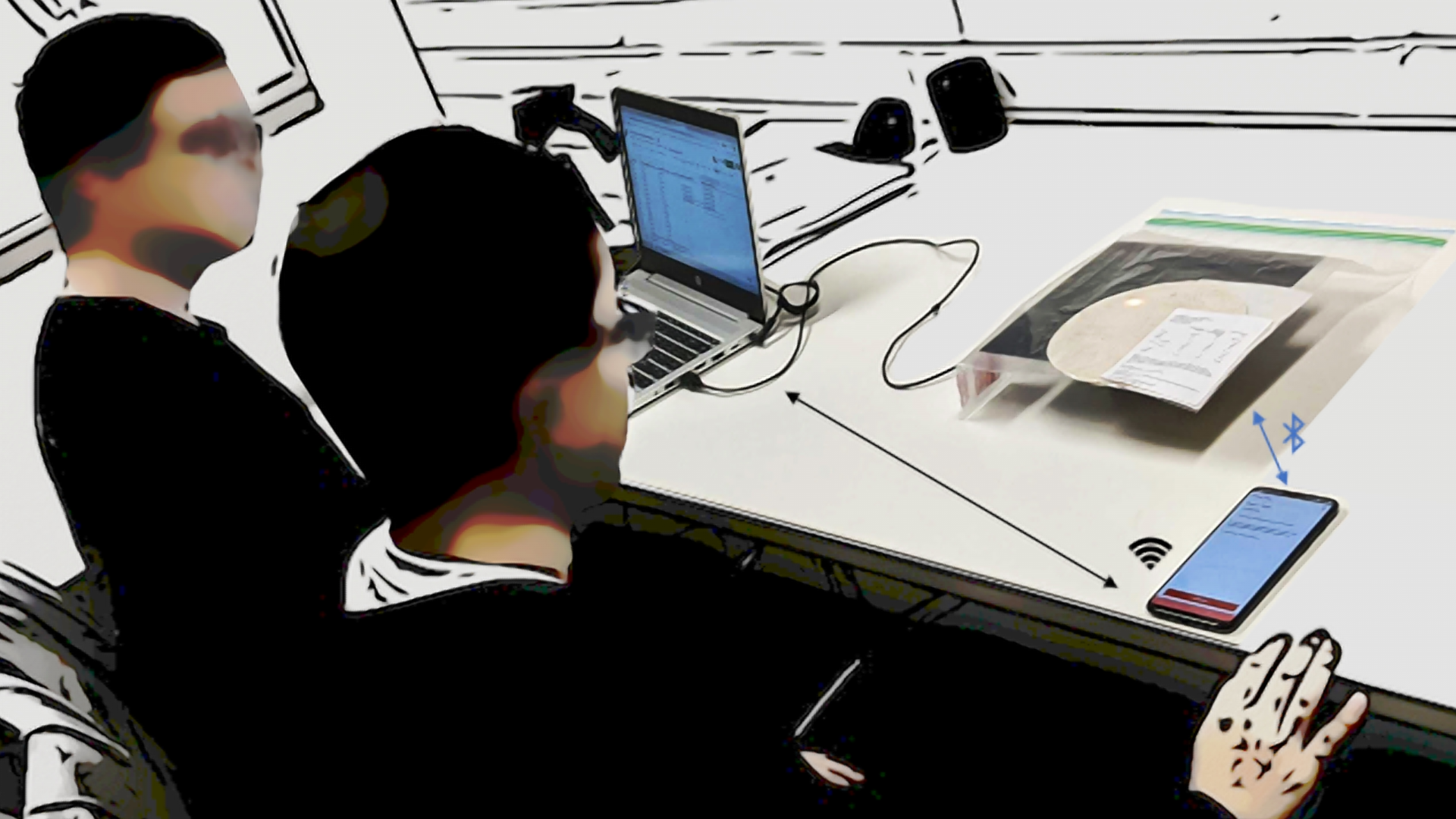
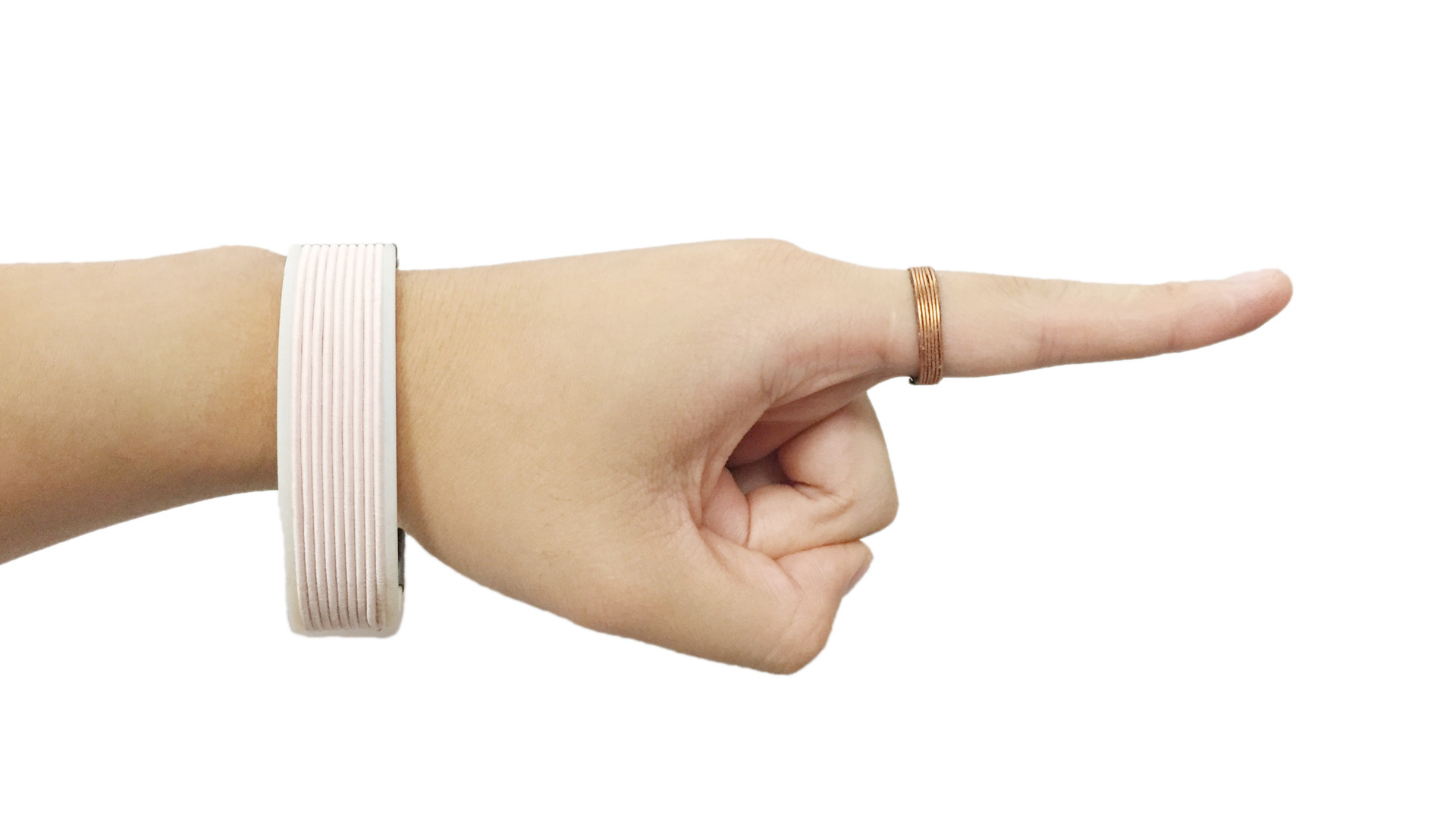
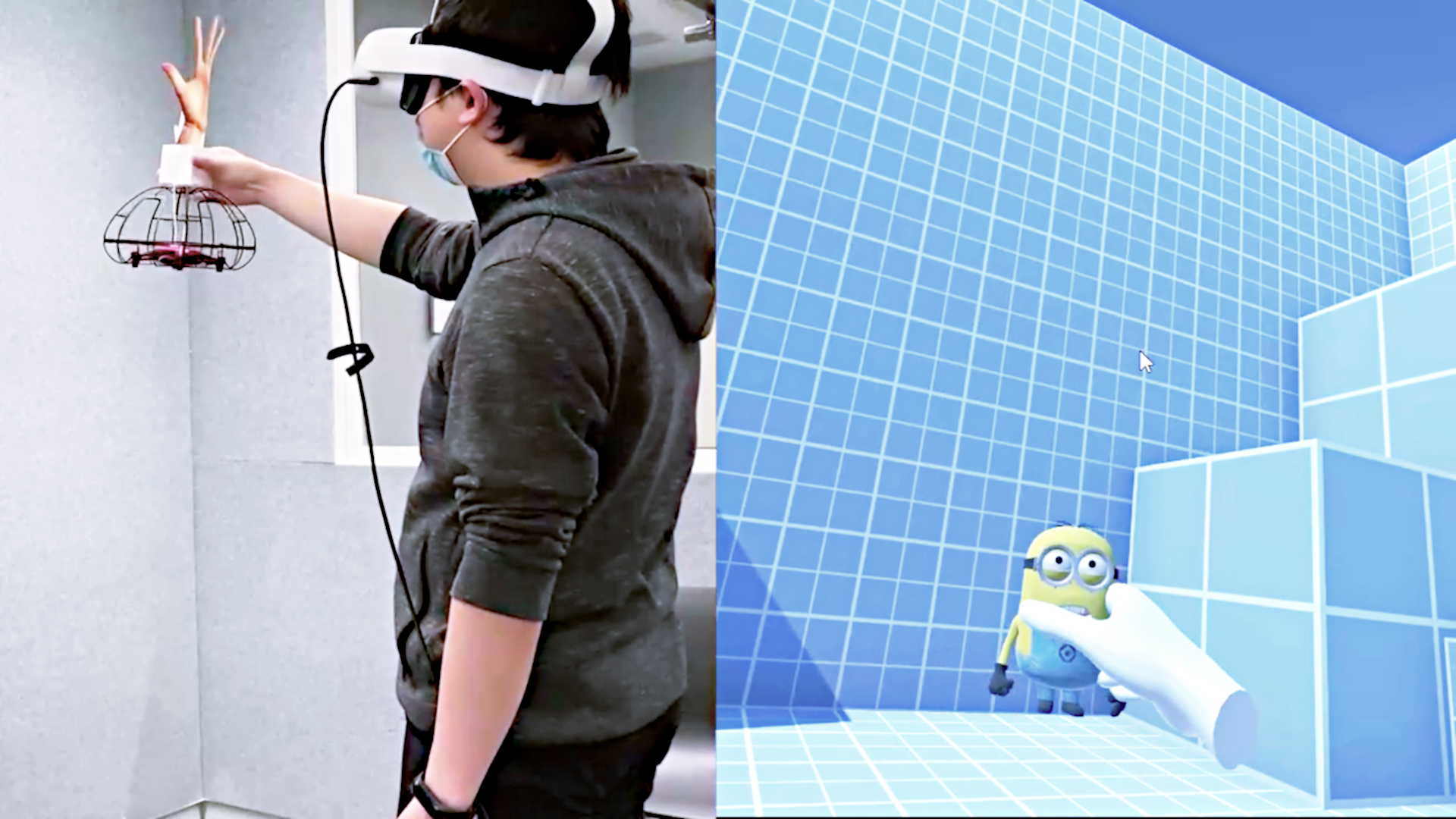
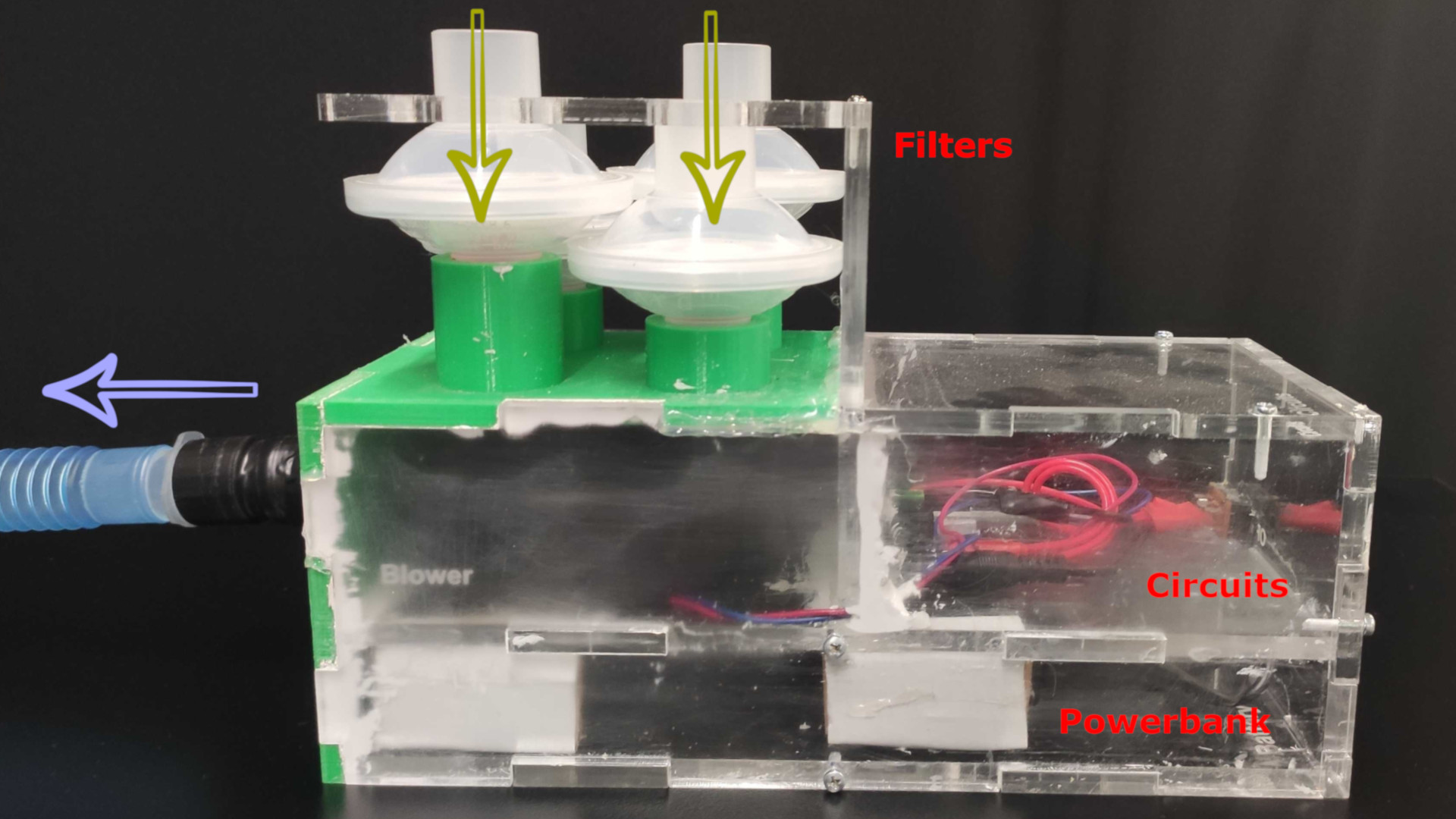
We present Knock the Reality, an interaction technique for virtual interface registration in mixed reality (MR). When a user knocks on a physical object, our technique identifies the object based on a knocking sound and registers a customizable virtual interface onto the object. Unlike computer vision-based methods, our approach does not require continuously processing image information. Instead, we utilize audio features which are less computationally expensive. This work presents our implementation and demonstrates an interaction scenario where a user works in MR. Overall, our method offers a simple and intuitive way to register MR interfaces.